Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Factors affecting depression and health-related quality of life in the elderly during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):520-529. Published online November 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0166
- 864 View
- 43 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 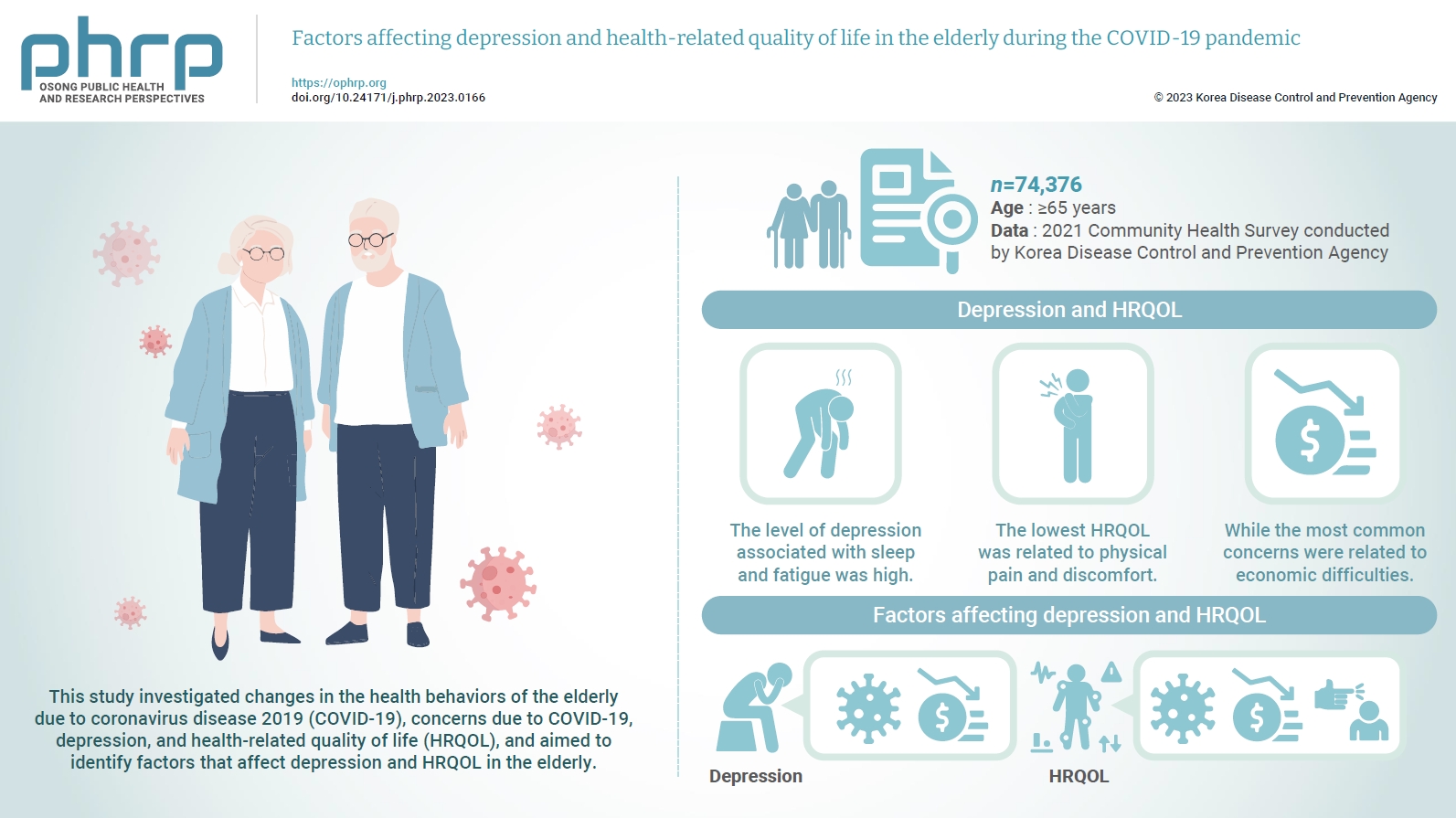
- Objectives
This study investigated changes in the health behaviors of the elderly due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), concerns due to COVID-19, depression, and healthrelated quality of life (HRQOL), and aimed to identify factors that affect depression and HRQOL in the elderly. Methods: This study was conducted using data from the 2021 Community Health Survey of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. From a total sample size of 229,242 individuals, 74,376 elderly people aged 65 or older were selected as subjects, and changes in health behaviors, concerns due to COVID-19, depression, and HRQOL were measured and analyzed. Results: The level of depression associated with sleep and fatigue was high. The lowest HRQOL was related to physical pain and discomfort, while the most common concerns were related to economic difficulties. Factors influencing depression included worries about infection and economic harm, while factors impacting HRQOL encompassed concerns about infection, economic harm, and criticism from others. Conclusion: If an infectious disease situation such as COVID-19 reoccurs in the future, it will be necessary to encourage participation in hybrid online and offline programs at senior welfare centers. This should also extend to community counseling institutions like mental health welfare centers. Additionally, establishing connections with stable senior job projects can help to mitigate the effects of social interaction restrictions, physical and psychological health issues, and economic difficulties experienced by the elderly.
- Effects of activities of daily living-based dual-task training on upper extremity function, cognitive function, and quality of life in stroke patients
- Hee-Su An, Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):304-313. Published online September 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0177
- 10,792 View
- 306 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of daily living dual-task training focused on improving attention and executive function of the upper extremities, cognitive function, and quality of life in stroke patients.
Methods
We included 30 stroke patients who were hospitalized between July 2020 and October 2020. They were divided into experimental and control groups through randomization. The experimental group performed 20 minutes of dual-task training and received 10 minutes of conventional occupational therapy, while the control group performed 20 minutes of single-task training and received 10 minutes of conventional occupational therapy. Both groups underwent their respective rehabilitation for 30 minutes per session, 5 times per week for 5 weeks.
Results
Both groups showed significant improvements in upper extremity function, cognitive function, and quality of life; the experimental group showed higher results for all items. A significant between-group difference was observed in the magnitude of the changes.
Conclusion
In stroke patients, dual-task training that combined attention and executive function with daily living activities was found to be meaningful, as it encouraged active participation and motivation. This study is expected to be used as a foundation for future interventions for stroke patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intervention and assessment of executive dysfunction in patients with stroke: A scoping review
Katsuya Sakai, Yuichiro Hosoi, Junpei Tanabe, Kathleen Bennett
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0298000. CrossRef - Occupation-based interventions to improve occupational performance and participation in the hospital setting: a systematic review
Gemma Wall, Stephen Isbel, Louise Gustafsson, Claire Pearce
Disability and Rehabilitation.2023; : 1. CrossRef - The effect of five activities daily living on improving cognitive function in ischemic stroke patients
Frana Andrianur, Dwi Prihatin Era, Arifin Hidayat, Ismansyah Ismansyah, Diah Setiani
Healthcare in Low-resource Settings.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Upper Limb Motor Rehabilitation on Cognition in Parkinson’s Disease: An Observational Study
Valentina Varalta, Elisa Evangelista, Anna Righetti, Giovanni Morone, Stefano Tamburin, Alessandro Picelli, Cristina Fonte, Michele Tinazzi, Ilaria Antonella Di Vico, Andreas Waldner, Mirko Filippetti, Nicola Smania
Brain Sciences.2022; 12(12): 1684. CrossRef
- Intervention and assessment of executive dysfunction in patients with stroke: A scoping review
- Impact of Mixed Cognitive Intervention Training on Early Onset Dementia
- Bo-Ra Jeon, Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(1):29-36. Published online February 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.1.05
- 5,431 View
- 218 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of mixed cognitive intervention training using spaced retrieval training, and errorless learning in participants with early onset dementia. This was based on reality orientation therapy for cognitive function, depression, and occupational performance of patients.
Methods Two early onset vascular dementia patients (> 65 years) with mild or moderate impairment were enrolled in a pre-test - post-test single-subject research design study. Prior to the study, the caregivers were interviewed about meaningful times, people, places, and areas of interest for the participant. A list of individual training words were selected based upon this information, and the participant was instructed to recall them after a 45-second, 90-second, 6-minute, and 12-minute delay. Baseline (3 sessions), intervention (20 sessions), and a second baseline period (3 sessions) were conducted. Activities of daily living were measured, and cognition was measured using the Consortium to Establish a Registry of Alzheimer’s Disease Korean version, whilst depression was measured using the Korean Form Geriatric Depression Scale, and task performance and satisfaction measured by the Canadian Occupational Performance Measure.
Results After intervention, both participants showed improvements in activities of daily living (ADL), word list memory/recognition, trail making A, occupational performance, and satisfaction improvement, which was clinically significant in 1 participant who also had a reduced score in the scale of depression classifying him as not depressed.
Conclusion Spaced retrieval training and errorless learning based on reality orientation therapy is an effective intervention in patients with early onset dementia and mild or moderate impairment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non‐pharmacological interventions for people living with young‐onset dementia and their carers: A scoping review focussing on the support of participants' needs
Iktae Kim, Yoosun Yang, Hongjin Cheon, Jiyeon Kim, Jun‐Ah Song
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 31(1): 14. CrossRef - Interventions for Persons with Young-Onset Dementia and Their Families: A Scoping Review
Xiaoyan Cui, Junqiao Wang, Bei Wu, Qianhua Zhao, Xueting Tang, Jing Wang
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2024; 97(4): 1519. CrossRef
- Non‐pharmacological interventions for people living with young‐onset dementia and their carers: A scoping review focussing on the support of participants' needs
- A Study on the Physical Activities, Mental Health, and Health-Related Quality of Life of Osteoarthritis Patients
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(6):368-375. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.6.07
- 6,023 View
- 235 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the physical activities, mental health, and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) of osteoarthritis patients.
Methods This study was conducted using data from the first year of the 7th Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. There were 8,150 participants included in the survey, and 665 participants had been diagnosed with osteoarthritis. This study analyzed the measurements of physical activities, depression, and HRQOL in participants with osteoarthritis.
Results The mean age of the participants was 67 ± 9.9 years and 83.1% were female. Participants rarely engaged in work-related physical activity, and engaged in leisure-related physical activities infrequently. Most of the participants (85.9%) did not do regular exercise, but 1/3 of the participants walked for over 10 minutes a day. “Pain/discomfort” had the least impact upon HRQOL, and among the depression subcategories, “difficult to sleep and tiredness” had the most impact. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that an adverse HRQOL score was statistically significantly associated with “location changes/physical activities” (
p < 0. 01), “depression” (p < 0.001) and “age” (p < 0.001).Conclusion Exercise programs should be in place which are manageable in everyday life for the elderly (> 65 years). Changes in daily routine so that patients become more active, should be supported by the family and community, together with assistance in managing psychological problems such as depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Predictors of Depression in Women with Osteoarthritis: Cross-Sectional Analysis of Nationally Representative Survey Data
Ananya Ravi, Elisabeth C. DeMarco, Sarah Gebauer, Michael P. Poirier, Leslie J. Hinyard
Healthcare.2024; 12(5): 502. CrossRef - A scalable 12-week exercise and education programme reduces symptoms and improves function and wellbeing in people with hip and knee osteoarthritis
Jemma L. Smith, Aidan Q. Innes, Danielle S. Burns, Davina Deniszczyc, James Selfe, Stephen MacConville, Kevin Deighton, Benjamin M. Kelly
Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Special Issue on Biomechanical and Biomedical Factors of Knee Osteoarthritis
Hanatsu Nagano
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(22): 11807. CrossRef - Investigation on the association between diabetes distress and productivity among patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus in the primary healthcare institutions
Yingqi Xu, Gabrielle Yin Yern Tong, Joyce Yu-Chia Lee
Primary Care Diabetes.2020; 14(5): 538. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Predictors of Depression in Women with Osteoarthritis: Cross-Sectional Analysis of Nationally Representative Survey Data
- The Effect of a Complex Intervention Program for Unilateral Neglect in Patients with Acute-Phase Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Hyun-Se Choi, Deok-Ju Kim, Yeong-Ae Yang
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(5):265-273. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.5.02
- 6,093 View
- 249 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The purpose of this study was to examine the combined effects of Prism Adaptation (PA) plus functional electrical stimulation (FES) on stroke patients with unilateral neglect, and suggest a new intervention method for acute-phase stroke patients.
Methods There were 30 patients included in this study from April to October 2016 that had unilateral neglect whilst hospitalized following a stroke (diagnosed by a professional). The participants, who were patients receiving occupational therapy, understood the purpose of the study and agreed to participate. The patients were randomly divided into 3 groups: PA plus FES group (Group A), PA group (Group B), and FES group (Group C). Treatments lasted for 50 minutes per day, 5 times per week, for 3 weeks in total. Reevaluation was conducted after 3 weeks of intervention.
Results All 3 groups showed unilateral neglect reduction after the intervention, but PA plus FES (complex intervention method) was more effective than PA or FES alone [effect size: Motor-free Visual Perception Test (0.80), Albert test (0.98), CBS (0.92)].
Conclusion The results of this study support further studies to examine complex intervention for the treatment of unilateral neglect.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inclusion of People With Aphasia in Stroke Trials: A Systematic Search and Review
Ciara Shiggins, Brooke Ryan, Farhana Dewan, Julie Bernhardt, Robyn O'Halloran, Emma Power, Richard I. Lindley, Gordon McGurk, Miranda L. Rose
Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.2024; 105(3): 580. CrossRef - Prism adaptation combined with eye movement training for unilateral spatial neglect after stroke: Study protocol for a single-blind prospective, randomized controlled trial
Yu-xuan Yang, Ling-ling Wang, Juan Du, Yao-min Luo, Yu-lei Xie, Bo Zhang, Han Zhang
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - No short-term treatment effect of prism adaptation for spatial neglect: An inclusive meta-analysis
Orsolya Székely, Antonia F. Ten Brink, Alexandra G. Mitchell, Janet H. Bultitude, Robert D. McIntosh
Neuropsychologia.2023; 189: 108566. CrossRef - A Complex Intervention Integrating Prism Adaptation and Neck Vibration for Unilateral Neglect in Patients of Chronic Stroke: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Hyun-Se Choi, Bo-Min Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(20): 13479. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological interventions for spatial neglect or inattention following stroke and other non-progressive brain injury
Verity Longley, Christine Hazelton, Calvin Heal, Alex Pollock, Kate Woodward-Nutt, Claire Mitchell, Gorana Pobric, Andy Vail, Audrey Bowen
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inclusion of People With Aphasia in Stroke Trials: A Systematic Search and Review
- The Effects of Restricted Physical Activity on Health-Related Quality of Life in Adult Patients with Depression
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(2):85-92. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.2.07
- 7,067 View
- 79 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The objective was to identify restricted physical activity in patients with depression, and to determine the effects of that restricted activity, on their health-related quality of life (HRQOL).
Methods Data was analysed from Year 1 of the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII-1). From a total sample of 8,150 subjects, 277 adults aged ≥19 years who were diagnosed with depression were selected. The results were derived using restricted activity and HRQOL data measured from the subjects.
Results Most of the participants were females ≥ 50 years old. HRQOL scores were high in the “self-care” dimension and low in the “pain/discomfort” and “anxiety/depression” dimensions. Their restricted activity due to illness in the past year, led to increases in participants being bedridden or absent from work. Many participants reported being bedridden for more than 3 months. A higher number of absences owing to illness in the past year, and longer durations of being bedridden, had a negative impact on HRQOL. Age, marital status, educational level, income level, and occupation were the sociodemographic variables that had an impact on HRQOL.
Conclusion Patients with depression experiencing stress in their daily lives should take measures to avoid illness and pain that may lead to them becoming bedridden, and employ lifestyle habits with support from families and community health promotion centres, where mental health counselling can be accessed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Childhood trauma, inflammatory biomarkers and the presence of a current depressive episode: Is there a relationship in subjects from a population study?
Leonardo Carvalho Oliveira, Natália Wirowski, Pedro Borges de Souza, Andressa Schneider Lobato, Karen Jansen, Taiane de Azevedo Cardoso, Thaíse Campos Mondin, Jean Pierre Oses, Flávio Kapczinski, Luciano Dias de Mattos Souza, Ricardo Azevedo da Silva, Fer
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2023; 158: 255. CrossRef - The Relationship between Physical Activity and Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults: The Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mun-Gyu Jun, Se-Hyeon Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(21): 2861. CrossRef
- Childhood trauma, inflammatory biomarkers and the presence of a current depressive episode: Is there a relationship in subjects from a population study?
- Effects of Physical Activity on Depression in Adults with Diabetes
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(4):143-149. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.4.02
- 5,769 View
- 145 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The purpose of this study was to identify the current state of physical activity in adults with diabetes and to investigate the effect of physical activity on depression.
Methods The present study was conducted using data from the 2nd year of the 6th Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. From the total of 7,550 individuals, 418 adults diagnosed with diabetes were selected as participants, and their physical activity and depression levels were examined.
Results The physical activity status of the participants showed that they did not usually engage in physical activities at work, and only a few participants were involved in moderate intensity physical leisure activity. Apart from walking for 10 minutes each day, which accounted for 1/3 of the participants, most of the participants did not engage in specific forms of exercise. An examination of the effects of physical activity on depression revealed that moderate intensity physical activity at work and leisure influenced depression. In terms of demographic characteristics, gender, occupation, income quintile, and subjective health status were all found to affect depression.
Conclusion For elderly (60 years or older) patients with diabetes, which accounted for the majority of the diabetic population, a systematic leisure program and professional education are necessary to help them to manage stress and depression in daily life. Additionally, provision of community and family support should encourage regular, moderate intensity exercise and promote lifestyle changes to encourage increased physical activity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of comorbid depression and associated factors among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Hunan, China
Rehanguli Maimaitituerxun, Wenhang Chen, Jingsha Xiang, Atipatsa C. Kaminga, Xin Yin Wu, Letao Chen, Jianzhou Yang, Aizhong Liu, Wenjie Dai
BMC Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Barriers & facilitators to physical activity in people with depression and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pakistan: A qualitative study to explore perspectives of patient participants, carers and healthcare staff
Aatik Arsh, Saima Afaq, Claire Carswell, Karen Coales, Najma Siddiqi
Mental Health and Physical Activity.2023; 25: 100542. CrossRef - Moderating Effect of Grip Strength in the Association between Diabetes Mellitus and Depressive Symptomatology
Diogo Veiga, Miguel Peralta, Élvio R. Gouveia, Laura Carvalho, Jorge Encantado, Pedro J. Teixeira, Adilson Marques
Sports.2023; 12(1): 3. CrossRef - Modeling the effects of physical activity, education, health, and subjective wealth on happiness based on Indonesian national survey data
Bhina Patria
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triad of impairment in older people with diabetes-reciprocal relations and clinical implications
A.H. Abdelhafiz, P.C. Davies, A.J. Sinclair
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 161: 108065. CrossRef - Association between exercise and health-related quality of life and medical resource use in elderly people with diabetes: a cross-sectional population-based study
Chien-Cheng Huang, Chien-Chin Hsu, Chong-Chi Chiu, Hung-Jung Lin, Jhi-Joung Wang, Shih-Feng Weng
BMC Geriatrics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Challenges and Strategies for Diabetes Management in Community-Living Older Adults
Alan J. Sinclair, Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Diabetes Spectrum.2020; 33(3): 217. CrossRef
- Prevalence of comorbid depression and associated factors among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Hunan, China
- Study on Cardiopulmonary Function, Maximal Oxygen Uptake, and Obesity Index according to Smoking Status in Middle-Aged and Older Office Workers
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(3):95-100. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.3.02
- 5,443 View
- 110 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To investigate the effect of smoking upon cardiopulmonary function, maximal oxygen uptake, and obesity index, in middle-aged and older workers to propose guidelines on healthcare for these age groups.
Methods This study analyzed medical data from 2,753 white-collar workers aged 50 years or older from workplaces located in Seoul, South Korea. Blood pressure (BP), resting heart rate, maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max), and body mass index (BMI) of each subject were measured. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS 21.0.
Results In the smoking group BP and resting heart rate were significantly higher than in the non-smoking and smoking-cessation groups (
p < 0.05). In addition, VO2max was lower in the smoking group compared to the other 2 groups. BP closely correlated with resting heart rate, abdominal fat ratio, and BMI. BMI was the highest in the group that stopped smoking and, BMI and abdominal fat ratio negatively correlated with VO2max.Conclusion Smoking increases the risk of cardiopulmonary disease but obesity may be caused by stopping smoking. Therefore, healthcare guidelines on smoking cessation should also include nutritional advice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Smoking Status on Bone Health and Osteoporosis Prevalence
Vu H. Nguyen
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2018; 9(4): 213. CrossRef
- Smoking Status on Bone Health and Osteoporosis Prevalence



 First
First Prev
Prev


